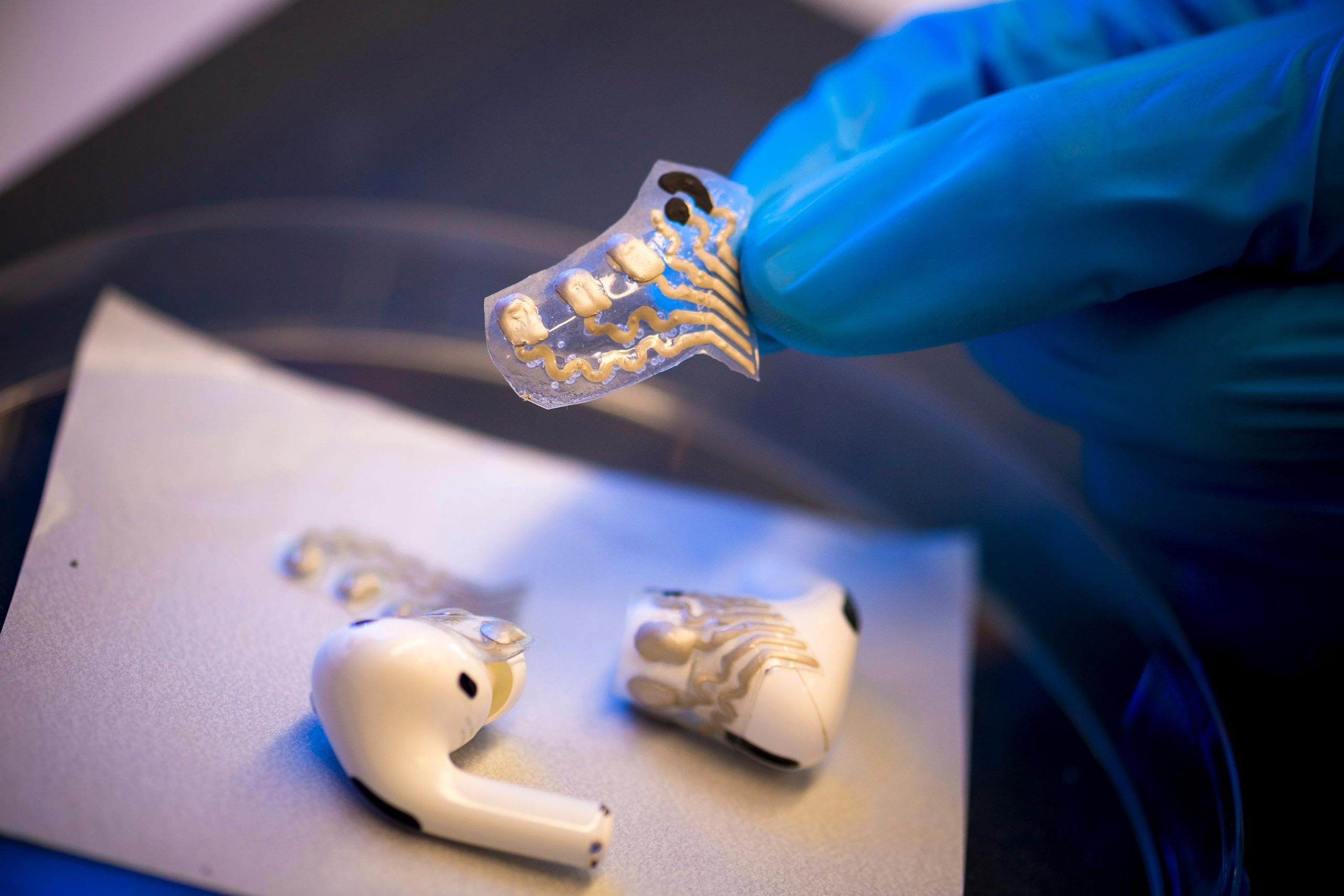
The screen-printed, versatile sensors are hooked up to the earbuds on a versatile, stamp-like floor. Credit score: Erik Jepsen/College of California San Diego
The streaming knowledge from these biosensors can be utilized for well being monitoring and prognosis of neuro-degenerative situations.
A pair of earbuds may be changed into a instrument to file {the electrical} exercise of the mind in addition to ranges of lactate within the physique with the addition of two versatile sensors screen-printed onto a stamp-like versatile floor.
The sensors can talk with the earbuds, which then wirelessly transmit the info gathered for visualization and additional evaluation, both on a smartphone or a laptop computer. The information can be utilized for long-term well being monitoring and to detect long-term neuro-degenerative situations.
The sensors, developed by a multidisciplinary analysis workforce of engineers on the College of California, San Diego, are lots much less cumbersome than state-of-the-art gadgets at present used to sense the mind’s electrical exercise and the physique’s sweat secretions. They can be utilized in the true world throughout train, the researchers confirmed.
Whereas in-ear sensing of a number of physiological parameters will not be new, integrating sensing of mind and physique alerts in a single platform is. The breakthrough was made potential by the mixed experience of biomedical, chemical, electrical, and nano-engineers.

The earbuds are inserted within the ear canal, the place they’ll harvest sweat and sensor the mind’s electrical exercise. Credit score: Erik Jepsen/College of California San Diego
Knowledge and Validation
Knowledge from an electroencephalogram (EEG), which measures electrical exercise within the mind, and sweat lactate, an natural acid the physique produces throughout train and regular metabolic exercise, may be mixed for quite a lot of functions. For instance, they can be utilized to diagnose various kinds of seizures, together with epileptic seizures. They may also be used for monitoring effort throughout bodily train and monitoring ranges of stress and focus.
The researchers validated the info collected throughout this proof-of-concept research in opposition to knowledge obtained from commercially out there dry contact EEG headsets and lactate-containing blood samples. The information the versatile sensors collected had been simply as efficient.
The workforce describes their work in an article showing on the quilt of the October 2023 challenge of Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The researchers foresee a future, during which neuroimaging and well being monitoring programs work with wearable sensors and cell gadgets, corresponding to telephones, earbuds, watches, and extra to trace mind exercise and ranges of many health-related metabolites all through the day. This may enable customers to reinforce mind and physique capabilities. The workforce additionally envisages a future during which the capabilities of present wearable audio gadgets, corresponding to earbuds, may be significantly expanded to assemble a a lot wider vary of knowledge.
“Having the ability to measure the dynamics of each mind cognitive exercise and physique metabolic state in a single in-ear built-in system that doesn’t intrude on the consolation and mobility of the consumer opens up super alternatives for advancing well being and wellness of individuals of all ages, anytime and anyplace,” stated Gert Cauwenberghs, a professor within the Shu Chien Gene Lay Division of Bioengineering at UC San Diego.
The sensors monitor the extent of lactate in sweat throughout train. Credit score: College of California San Diego
Why Earbuds?
The workforce felt that the ever-present sporting of earbuds translated to an untapped potential for gathering mind and physique alerts conveniently, each for wellness and well being.
“Earbuds have been round for many years, and in some ways had been one of many first wearable gadgets available on the market,” stated Patrick Mercier, a professor within the UC San Diego Division of Electrical and Pc Engineering. “This analysis takes necessary first steps to indicate that impactful knowledge may be measured from the human physique just by augmenting the capabilities of earbuds that individuals already use every day. Since there are not any main frictions to utilizing this know-how, we anticipate eventual extensive scale adoption.”
The ear has sweat glands and is near the mind, stated Yuchen Xu, co-first creator of the paper, and a postdoctoral researcher in Cauwenberghs’s lab. “It’s a pure entry level–persons are used to sporting earbuds,” he stated.
Constructing the Sensors
Such a system requires multi-domain experience, which is how this mission took place within the Heart for Wearable Sensors at UC San Diego the place bioengineering professor Cauwenberghs collaborated with nanoengineering professors Joseph Wang and Sheng Xu, who’ve in depth expertise in designing and constructing stretchable, versatile, and high-performance chemical sensors. Patrick Mercier, a professor within the Jacobs Faculty Division of Electrical and Pc Engineering, additionally lent his in depth expertise in low-power biomedical electronics and wi-fi programs to the mission.
“One of many the reason why we had been capable of obtain this breakthrough was that we actually considered integration,” stated Ernesto De La Paz, a Ph.D. alumnus from the analysis group of nanoengineering Professor Joseph Wang, and co-first creator of the paper. “We wished to make the sensors as small as potential to gather tiny sweat samples. We additionally accounted for the irregular form of the ear by integrating parts that may bend.”
Step one in constructing the in-ear sensors was confirming that EEG and lactate knowledge could possibly be gathered within the ear. Researchers needed to design smaller, extra compact devices to assemble electrophysiological alerts, corresponding to EEG knowledge, that will match on an earbud. In addition they needed to discover a appropriate materials to gather sweat and sense lactate. After preliminary experiments on human topics, researchers decided that the most effective location to gather and file lactate knowledge was the tragus, the place sweat accumulates on the entrance of the ear. The workforce additionally knew from earlier expertise that to gather EEG knowledge, high-performance physiological electrodes pointed towards the temporal lobe had been required.
“The first technical problem was not solely becoming two sensors within the ear, which is a small house that varies from one particular person to a different, but in addition reliably buying alerts from each EEG and lactate,” stated Yuchen Xu. “We additionally needed to accommodate for earbuds integration and scale back crosstalk. That’s after we landed on the thought of a stamp-like stretchable sensor, which is a straightforward addition to the earbud itself, however has all the required features we wanted and gave us sufficient freedom for our designs.”
To guarantee that the electrophysiological sensors had agency contact with the ear, researchers designed 3D, spring-loaded sensors that maintain contact however can alter as earbuds transfer. However, to enhance sweat assortment, researchers coated the electrochemical sensors with a see-through hydrogel movie. “It’s sponge-like and hydrophilic,” Yuchen Xu stated. “It acts as a mechanical cushion between pores and skin and sensors and in addition helps accumulate sweat.”
It’s tough to keep away from crosstalk between the 2 sensors given the restricted house contained in the ear. Researchers analyzed varied materials picks, structural designs and validated the feasibility of concurrently recording EEG and lactate alerts with two sensors separated by two millimeters.
“This new and highly effective in-ear multimodal wearable bioelectronic platform affords a wealthy supply of real-time info on the well being of the customers, by recording concurrently and dynamically bodily and biochemical info,” stated Joseph Wang, a professor within the Division of NanoEngineering and director of the Heart for Wearable Sensors on the Jacobs Faculty.
Future Alternatives
One of many gadgets’ limitations is that with a purpose to collect sufficient lactate to meaningfully analyze knowledge, topics must carry out train or different bodily exercise that get folks to sweat. In future work, researchers will purpose to cast off this requirement.
“The following step can be to combine electronics into the sensor,” Yuchen Xu stated.
The workforce can be engaged on processing the info on the system itself. In the end, the objective is to transmit the processed knowledge wirelessly to a pc or a smartphone. In-ear sensors might additionally collect extra knowledge, corresponding to oxygen saturation ranges and glucose ranges.
The researchers envision this work to result in new therapies.
“Auditory neurofeedback coupling the measured mind alerts with sound performed by the system within the ear could allow doubtlessly far-reaching new therapeutic advances for energetic remediation of debilitating neurological issues, corresponding to tinnitus for which at present no efficient therapy is accessible,” Cauwenberghs stated.
Sensor Analysis
All through the research, researchers performed in depth experiments to validate the efficacy of the sensors.
They characterised the electrode efficiency in addition to a number of outstanding mind sign patterns, together with alpha modulation and auditory steady-state responses, along with electrooculography (EOG) for the electrophysiological sensors.
They characterised the sensitivity, selectivity, and long-term stability of lactate sensors.
In addition they characterised crosstalk between sensors, mechanical stability, and environmental stability for the built-in sensors.
“The ear canal has been comparatively underexplored throughout the wearable know-how neighborhood,” stated Sheng Xu, a college member within the Jacobs Faculty Division of NanoEngineering. “This work demonstrates the potential of steady sensing to seize invaluable bodily and chemical alerts from the ear canal thereby paving the way in which for quite a few thrilling alternatives within the area of wearables.”
Reference: “Unobtrusive in-ear built-in physiological and metabolic sensors for steady brain-body exercise monitoring” by Yuchen Xu, Ernesto De la Paz, Akshay Paul, Kuldeep Mahato, Juliane R. Sempionatto, Nicholas Tostado, Min Lee, Gopabandhu Hota, Muyang Lin, Abhinav Uppal, William Chen, Srishty Dua, Lu Yin, Brian L. Wuerstle, Stephen Deiss, Patrick Mercier, Sheng Xu, Joseph Wang and Gert Cauwenberghs, 28 September 2023, Nature Biomedical Engineering.
DOI: 10.1038/s41551-023-01095-1
UC San Diego Shu Chien-Gene Lay Division of Bioengineering: Yuchen Xu, Akshay Paul, Min Lee, Abhinav Uppal, William Chen, Stephen Deiss, Gert Cauwenberghs
UC San Diego Division of NanoEngineering and Chemical Engineering: Ernesto De la Paz, Kuldeep Mahato, Juliane R. Sempionatto, Nicholas Tostado, Muyang Lin, Srishty Dua, Lu Yin, Sheng Xu, Joseph Wang
UC San Diego Division of Electrical and Pc Engineering: Gopabandhu Hota, Brian L. Wuerstle, Patrick Mercier
This analysis was carried out at, and supported by, the Heart for Wearable Sensors on the UC San Diego Jacobs Faculty of Engineering.


/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24956079/Worldcoin_orb.jpg)


/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13292779/acastro_181017_1777_brain_ai_0002.jpg)