El Niño is a local weather cycle within the Pacific Ocean which impacts climate patterns world wide.
The cycle begins when heat water within the western tropical Pacific Ocean shifts eastward alongside the equator towards the coast of South America. Usually, this heat water swimming pools close to Indonesia and the Philippines. Throughout an El Niño, the Pacific’s warmest floor waters sit offshore of northwestern South America.
The placement of tropical storms shifts eastward throughout an El Niño as a result of atmospheric moisture is gas for thunderstorms, and the best quantity of evaporation takes place above the ocean’s warmest water.
The other of El Niño is La Niña, which is when the waters of the tropical jap Pacific are colder than regular and commerce winds blow extra strongly than regular.
Collectively, El Niño and La Niña are components of an oscillation within the ocean-atmosphere system referred to as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO cycle, which additionally has a impartial part.
How lengthy will El Niño final?
El Niños happen each three to 5 years however could come as continuously as each two years or as not often as each seven years. Sometimes, El Niños happen extra continuously than La Niñas. Every occasion normally lasts 9 to 12 months. They typically start to type in spring, attain peak power between December and January, after which decay by Might of the next yr.
Local weather scientists at NOAA say there’s a greater than 95% likelihood that the present El Niño occasion will persist into 2024. They count on warmer-than-average situations that can progressively strengthen into the Northern Hemisphere’s fall and winter.
What causes El Niño?
Scientists don’t but perceive intimately what triggers an El Niño cycle. Not all El Niños are the identical, nor do the ambiance and ocean all the time comply with the identical patterns from one El Niño to a different.
To forecast an El Niño, scientists monitor a number of areas throughout the Pacific.
“You must consider every area as an ocean sloshing round,” mentioned Neville Sweijd, director of the Alliance for Collaboration on Local weather and Earth Programs Science (ACCESS) in South Africa. “Generally it sloshes to 1 aspect, and generally it sloshes to the opposite. That is El Niño and La Niña.”
Consultants “monitor the typical sea-surface temperature in every area and use that to type a mannequin,” he instructed Dwell Science. “The fashions will then predict the chance of the manifestation.”
In regular, non-El Niño situations, commerce winds blow towards the west throughout the tropical Pacific, away from South America. These winds pile up heat floor water within the western Pacific in order that the ocean floor is about 1.5 toes (0.5 meters) increased offshore Indonesia than it’s offshore Ecuador. Larger sea-surface temperature causes water ranges to increase and rise, and likewise shifts rainfall from land to ocean.
In a non El Niño yr, the sea-surface temperature can be about 14 levels Fahrenheit (8 levels Celsius) hotter within the western Pacific. Cooler ocean temperatures dominate offshore northwest South America, because of an upwelling of chilly water from deeper ranges.
Forecasters declare an official El Niño once they see each ocean temperatures and rainfall from storms veer to the east. Consultants who monitor El Niño additionally search for prevailing commerce winds to weaken. These modifications arrange a suggestions loop between the ambiance and the ocean that enhances El Niño situations.
What’s the El Niño forecast for the 2023-2024 winter?
After months of warning, on June 8, scientists on the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) confirmed the arrival of the newest El Niño occasion.
El Niño for the 2023-2024 winter is forecast to be very sturdy, which suggests regular sea-surface temperatures within the Pacific Ocean are anticipated to deviate dramatically from their regular averages. Nonetheless, their power doesn’t instantly correspond to the severity of their impacts, as this relationship can fluctuate significantly between cycles.
“Their results fluctuate relying on the depth, period, time of yr when it develops, and the interplay with different modes of local weather variability,” mentioned Álvaro Silva, a local weather knowledgeable on the World Meteorological Group. “Not all areas of the world are affected, and even inside a area, the impacts might be completely different.”
The present El Niño occasion is anticipated to push international temperatures into uncharted territory and contribute to international warming crossing the essential 2.7 F (1.5 C) threshold throughout the subsequent 5 years. It’s going to almost certainly intensify excessive climate occasions related to local weather change — reminiscent of warmth waves, drought and heavy rainfall — in sure areas.
“El Niño is a robust contributing issue to a number of the extremes now we have skilled prior to now and that we’re more likely to expertise within the subsequent months,” Silva instructed Dwell Science. “It is vitally doubtless that this yr or subsequent yr we are going to see the warmest yr on report.”
Does El Niño trigger extra rain, or drought?
Throughout an El Niño, the commerce winds weaken within the central and western Pacific. Floor water off South America warms up as a result of there’s much less upwelling of the chilly water from under to chill the floor. The clouds and rainstorms related to heat ocean waters additionally shift eastward. The nice and cozy waters launch a lot power into the ambiance that climate modifications everywhere in the planet.
An El Niño creates stronger wind shear and extra steady air over the Atlantic, which makes it tougher for hurricanes to type there. Nonetheless, the warmer-than-average ocean temperatures enhance jap Pacific hurricanes, contributing to extra lively tropical storm seasons.
Robust El Niños are additionally related to above-average precipitation within the southern United States. The cloudier climate usually causes below-average winter temperatures in that a part of the nation, whereas temperatures tilt hotter than common within the northern U.S. Rainfall is commonly under common within the Ohio and Tennessee valleys and the Pacific Northwest throughout an El Niño, in line with NOAA.
Document rainfall typically strikes Peru, Chile and Ecuador throughout an El Niño yr. Fish catches offshore South America are usually decrease than regular as a result of the marine life migrates to the north and south, following colder water.
El Niño additionally impacts precipitation in different areas, together with Indonesia and northeastern South America, which have a tendency towards drier-than-normal situations. Temperatures in Australia and Southeast Asia run hotter than common. El Niño-caused drought might be widespread, affecting southern Africa, India, Southeast Asia, Australia, the Pacific Islands and the Canadian prairies.
In contrast to El Niño, La Niña occasions are characterised by a sustained cooling impact across the equator and jap tropical Pacific. This typically ends in stronger and extra frequent hurricanes throughout North America and may result in heavy flooding in lots of Pacific Island nations, in addition to droughts alongside the west coast of South America.
What had been previous El Niño years like?
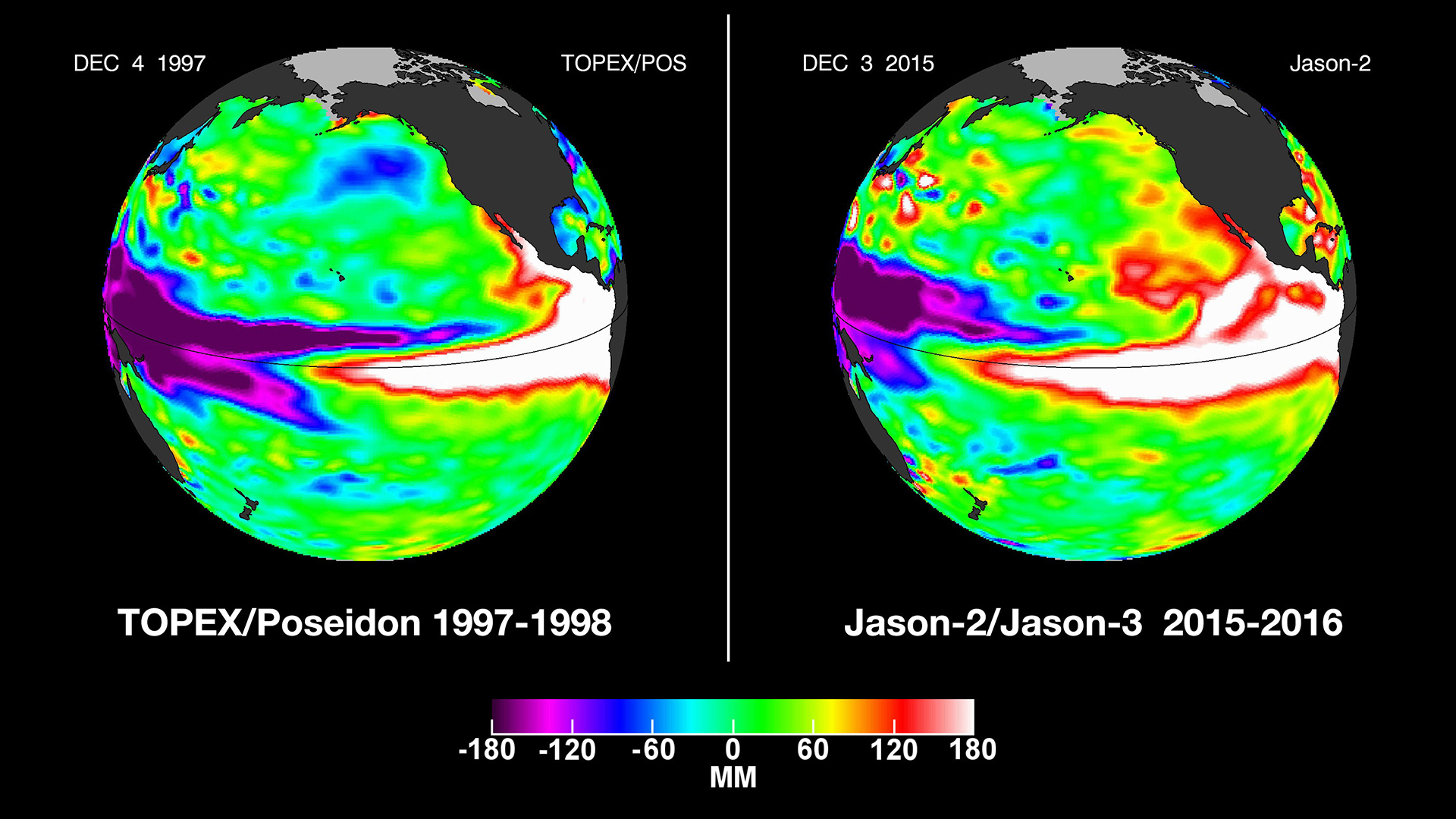
The final El Niño occasion occurred between February and August 2019, however its impacts had been comparatively weak. One of many strongest in current a long time was the El Niño that developed within the winter of 1997 to 1998. It resulted in 1000’s of deaths and accidents from extreme storms, heatwaves, floods, fires and drought. In the US, devastating storms within the south broken infrastructure and crops, whereas the north skilled above-normal temperatures and little or no rain and snowfall.
Between July 2020 and March 2023, a uncommon triple-dip La Niña upended climate patterns world wide. The three-year occasion was partly answerable for record-breaking rain and extreme flooding in Australia, a record-breaking Atlantic hurricane season in 2020 and the third most lively hurricane season in 2021.