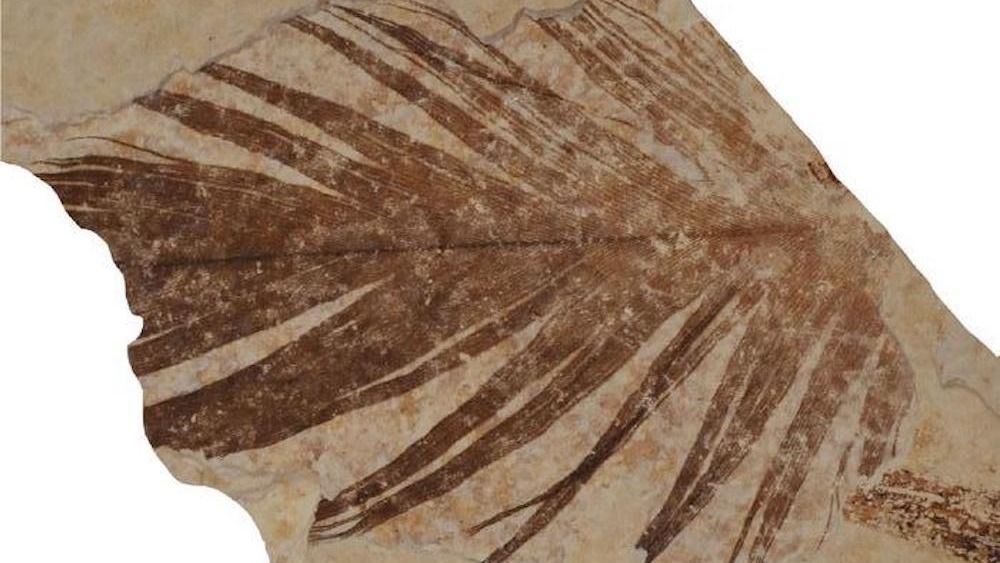
125 million-year-old dinosaur feathers had been remarkably just like trendy chook feathers, evaluation reveals

Feathers from modern-day birds have extra in widespread with dinosaur feathers than specialists beforehand thought and have the same protein composition, a brand new X-ray evaluation reveals. The invention affords new perception into the evolution of feathers over a whole bunch of thousands and thousands of years.
Paleontologists examined feathers from three historical animals, together with a 125 million-year-old nonavian dinosaur known as Sinornithosaurus present in China; a 125 million-year-old early chook, additionally from China, often known as Confuciusornis; and an unspecified species that lived in what’s now the Inexperienced River Formation in Wyoming 50 million years in the past, in keeping with a examine printed Sept. 21 within the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
After conducting X-ray and infrared mild analyses on the traditional feathers, the researchers detected traces of corneous beta-proteins (CBPs), previously often known as beta-keratins, that are proteins vital for strengthening feathers for flight. The worldwide group of researchers then examined feathers from right this moment’s birds, equivalent to zebra finches (Taeniopygia) and seen that they contained the same chemical construction.
Associated: Scientists modified scales on hen ft to feathers by tweaking a single gene
“These similar beta proteins are additionally current in trendy chook feathers,” lead examine writer Tiffany Slater, a postdoctoral researcher of paleobiology at College Faculty Cork in Eire, informed Dwell Science.
Previous to this examine, scientists thought historical animal feathers had a very totally different protein composition and had been primarily composed of alpha proteins, which are not as sturdy as CBPs. Nevertheless, this new examine confirmed that not solely had been the outdated feathers primarily made up of CBPs however that these proteins remodeled into alpha proteins throughout fossilization, in keeping with a assertion.
“The dinosaur feathers we analyzed present that they principally encompass beta proteins,” Slater stated. “So, the unique report that historical feathers had been predominately composed of alpha proteins was seemingly an artifact of fossilization.”
This new pondering not solely exhibits that proteins can stay preserved within the fossil report for upward of 125 million years but in addition gives new pondering into the evolution of historical feathers by “pushing the time scales lots additional than what we thought,” Slater stated.
“The chemistry of modern-day feathers is definitely much more historical than we beforehand thought,” Slater stated. “Our analysis helps rewrite the narrative and exhibits that the very fundamental constructing blocks which can be required for powered flight had been current no less than 125 million years in the past.”
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24874226/236757_iRobot_s_two_newest_Roombas_br_WJoel.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16125019/acastro_190416_1777_music_ai_0001.0.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13292779/acastro_181017_1777_brain_ai_0002.jpg)
