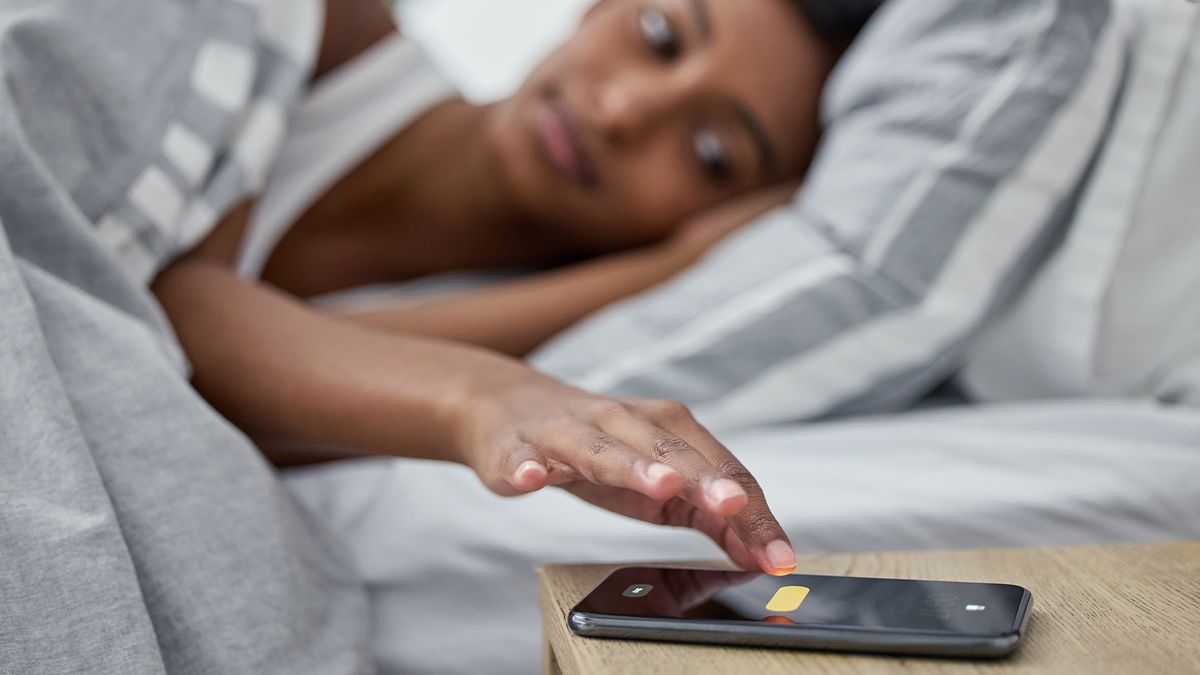
Do you often hit the “snooze” button when your alarm blares within the morning? Excellent news: You are not alone, and people further Zs may increase your cognitive efficiency if you first rise up, new analysis suggests.
In a research of greater than 1,700 surveyed adults worldwide, revealed Wednesday (Oct. 18) within the Journal of Sleep Analysis, 69% stated they hit the snooze button or set a number of alarms no less than “typically.”
Then, in an experiment with 31 recurring “snoozers,” the research authors discovered that hitting snooze improved a few of these people’ efficiency on cognitive checks. Nonetheless, it did not seem to influence their temper, how sleepy they felt within the morning or the conventional improve within the stress hormone cortisol that occurs throughout the first hour of waking and helps put together the physique for the day forward.
“Snoozing for half-hour within the morning doesn’t have any main detrimental results on the sleep that evening or how drained one feels when waking up,” Tina Sundelin, lead research writer and psychologist at Stockholm College in Sweden, informed Stay Science in an e mail. “For many who are drowsy within the morning, akin to night individuals, and discover that snoozing helps them get up, the research exhibits that they could really be extra objectively alert [meaning that they performed better on the cognitive tests] after snoozing — even when they do not really feel kind of sleepy,” she stated.
Associated: Scientists might have discovered the lacking hyperlink between coronary heart illness and sleep issues
Getting a great evening’s sleep is essential for our basic well being and well-being, however many individuals commonly do not get sufficient sleep. About one-third of U.S. adults report sleeping lower than the advisable seven or extra hours an evening. Some individuals hit snooze to ease the sting of waking up abruptly or to get a number of further minutes of sleep, however little is understood in regards to the well being impacts of this behavior.
Within the new research, 1,732 adults had been requested to explain their waking habits. On common, the individuals who reported no less than occasional snoozing spent round 22 minutes sleeping after their first alarm went off. These people had been round six years youthful and nearly 4 occasions extra more likely to be evening owls than those that reported that they by no means hit snooze, the authors discovered. They had been additionally extra more likely to sleep for a shorter time period in the course of the evening and to expertise drowsiness within the morning than non-snoozers.
For the 31 common snoozers within the second leg of the research, snoozing for half-hour both improved or did not have an effect on their efficiency on cognitive checks they accomplished once they awakened, in contrast with once they weren’t allowed to snooze. These checks included primary arithmetic questions and having to memorize an inventory of phrases and later acknowledge them amongst new phrases.
When allowed to snooze, the individuals had been much less more likely to get up from the deepest stage of sleep — known as slow-wave sleep — than they had been once they needed to get up straight away. Waking throughout slow-wave can result in sleep inertia, that means the groggy feeling you get because the physique transitions from sleep to waking.
The research was restricted in that the experiment was small and the survey portion relied on individuals self-reporting their sleeping and waking habits. Nonetheless, the crew hopes the findings will open doorways for future analysis into individuals’s waking habits, such because the alternative ways through which snoozers get up.
“Maybe one thing like a light-weight alarm (the type that slowly makes the room brighter) would work in an analogous means however with out having a number of abrupt wakeups,” Sundelin stated. The crew would additionally wish to discover the potential long-term results of snoozing and to check “excessive snoozers,” who snooze for as much as two hours every morning, she stated.
This text is for informational functions solely and isn’t meant to supply medical recommendation.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24018613/STK325_K_Radtke_Sony_01.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22024805/dbohn_201109_4283_0009.0.jpg)